Pregnancy is a time of excitement and transformation, but it also comes with health checks and medical terms that can sound overwhelming. One such term you may hear during a scan is “low-lying placenta.” While it can sound alarming, a low-lying placenta is quite common in early pregnancy — and in most cases, it resolves naturally as the baby grows.
In this article, we’ll explore what a low-lying placenta is, how to recognize its symptoms, what risks it may pose, and when to seek help.
What Is a Low-Lying Placenta?
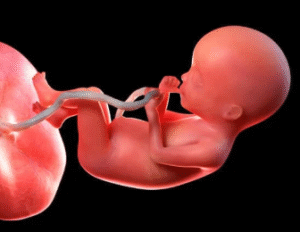

A low-lying placenta refers to a situation where the placenta is implanted in the lower part of the uterus and is close to, or partially covering, the cervix. This is often detected during a routine second-trimester ultrasound scan (usually between 18 and 21 weeks). In most cases, the placenta gradually “moves up” as the uterus expands, creating a clear path for vaginal delivery.
However, if the placenta remains too close to the cervix after 32 weeks, the condition is classified as placenta previa, which may require closer monitoring or a caesarean delivery.
Common Symptoms of a Low-Lying Placenta
In many cases, a low-lying placenta doesn’t cause any symptoms at all — especially in the early stages of pregnancy. However, as the pregnancy progresses, certain signs may indicate that the placenta is too close to the cervix:
Painless Vaginal Bleeding
The most common symptom is bright red vaginal bleeding in the second or third trimester. It often occurs without warning and without pain. This bleeding may be light or heavy and sometimes follows sexual intercourse or physical exertion.
Pelvic Pressure or Discomfort

Some women may experience a feeling of pressure or discomfort in the pelvic region, particularly if the placenta is pressing on the cervix or surrounding structures.
Unusual Baby Position
A baby lying in a breech (bottom-down) or transverse (sideways) position can be a clue to an abnormally placed placenta. This is because the placenta may be blocking the space needed for the baby to turn into a head-down position.
Mild Cramping Without Contractions
While not always present, dull cramping or a sense of “pulling” in the lower abdomen might be associated with changes in placental position or minor irritation near the cervix.
No Symptoms at All
It’s important to understand that many women with a low-lying placenta have no symptoms and only find out during a routine scan. That’s why regular antenatal appointments and ultrasound scans are crucial.
What Causes a Low-Lying Placenta?
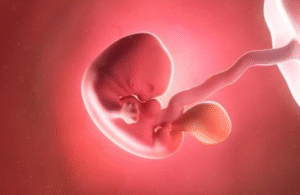

While there is no single known cause, certain risk factors may increase the chance of developing this condition:
- Previous cesarean section or uterine surgery
- Pregnancy with twins or multiples
- Smoking or drug use during pregnancy
- Use of assisted reproductive technology (e.g., IVF)
- Being over the age of 35
- History of placenta previa in earlier pregnancies
How Is It Diagnosed?
A low-lying placenta is usually diagnosed during your mid-pregnancy anomaly scan. If the placenta is within 2 cm of the cervix, your doctor may recommend another scan at 32 weeks and possibly again at 36 weeks to check if the placenta has moved upwards.
A transvaginal ultrasound may be used for a more accurate assessment of the placenta’s position — it’s safe and does not harm the baby.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Contact your doctor or maternity unit immediately if you experience:
- Any vaginal bleeding (light or heavy)
- Severe abdominal pain or cramping
- Dizziness or fainting along with bleeding
- Reduced fetal movement
- Signs of early labor (contractions or fluid leak)
Even if the bleeding is light and painless, it should never be ignored during pregnancy.
Can You Still Have a Normal Delivery?
In about 90% of cases, the placenta moves up as the uterus stretches, and vaginal birth becomes possible. However, if the placenta remains low, especially after 36 weeks, a planned cesarean section is often the safest option to avoid complications such as hemorrhage during labor.
Final Thoughts
While a diagnosis of a low-lying placenta may sound concerning, it’s important to remember that most women go on to have safe pregnancies and healthy babies. The key lies in early detection, regular follow-up scans, and following your doctor’s advice.
Pay close attention to your body, attend all prenatal appointments, and seek help if you notice any unusual symptoms. With the right care and monitoring, the journey to motherhood can remain smooth and joyful.




