Follicle growth plays a crucial role in the success of in vitro fertilization (IVF). The development of healthy, mature follicles is necessary for egg retrieval and fertilization. However, in some cases, follicles may grow slower than expected, leading to challenges in IVF treatment. Understanding the reasons behind slow follicular growth can help optimize fertility treatments and improve outcomes.
In this article, we’ll discuss what follicle growth is, why it happens, its impact on IVF success, and the top 10 reasons why some follicles grow slower than expected.
What is Follicle Growth in IVF?
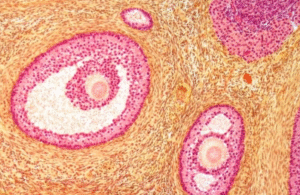

Follicles are small fluid-filled sacs in the ovaries that contain immature eggs. Each menstrual cycle, several follicles begin to develop, but only one (or sometimes more in assisted reproductive techniques like IVF) matures enough to release an egg during ovulation.
During IVF, hormone medications are used to stimulate multiple follicles to grow at the same time, increasing the number of eggs available for fertilization. The ideal follicle size for egg retrieval is typically between 16–22 mm, as this indicates that the egg inside has reached maturity.
Why Does Follicle Growth Happen?
Follicular development is driven by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which stimulates the ovaries to produce multiple follicles. The growth process is carefully monitored through ultrasound scans and blood tests to ensure optimal conditions for egg retrieval.
Factors such as hormone levels, ovarian health, and overall reproductive function play a role in follicle growth. When follicles grow at the right pace, they produce mature eggs, increasing the chances of successful fertilization and embryo development. However, if follicle growth is slow, it may reduce the number of viable eggs for IVF, affecting overall success rates.
Impact of Slow Growing Follicles on IVF – Why Follicle Growth is Slow?
Slow-growing follicles can have significant consequences in IVF treatment:
- Lower Egg Yield: Fewer mature eggs available for retrieval may reduce the chances of fertilization.
- Poor Egg Quality: Eggs from underdeveloped follicles may have lower quality, affecting embryo viability.
- Cycle Cancellation: If too few follicles mature, the IVF cycle may be canceled or postponed.
- Increased Medication Use: Additional stimulation drugs may be required, increasing costs and side effects.
- Lower Pregnancy Success Rates: A reduced number of mature eggs can impact fertilization, implantation, and pregnancy outcomes.
Identifying and addressing the underlying causes of slow follicular growth is essential to improving IVF success.
Top 10 Reasons for Slow Growing Follicles in IVF
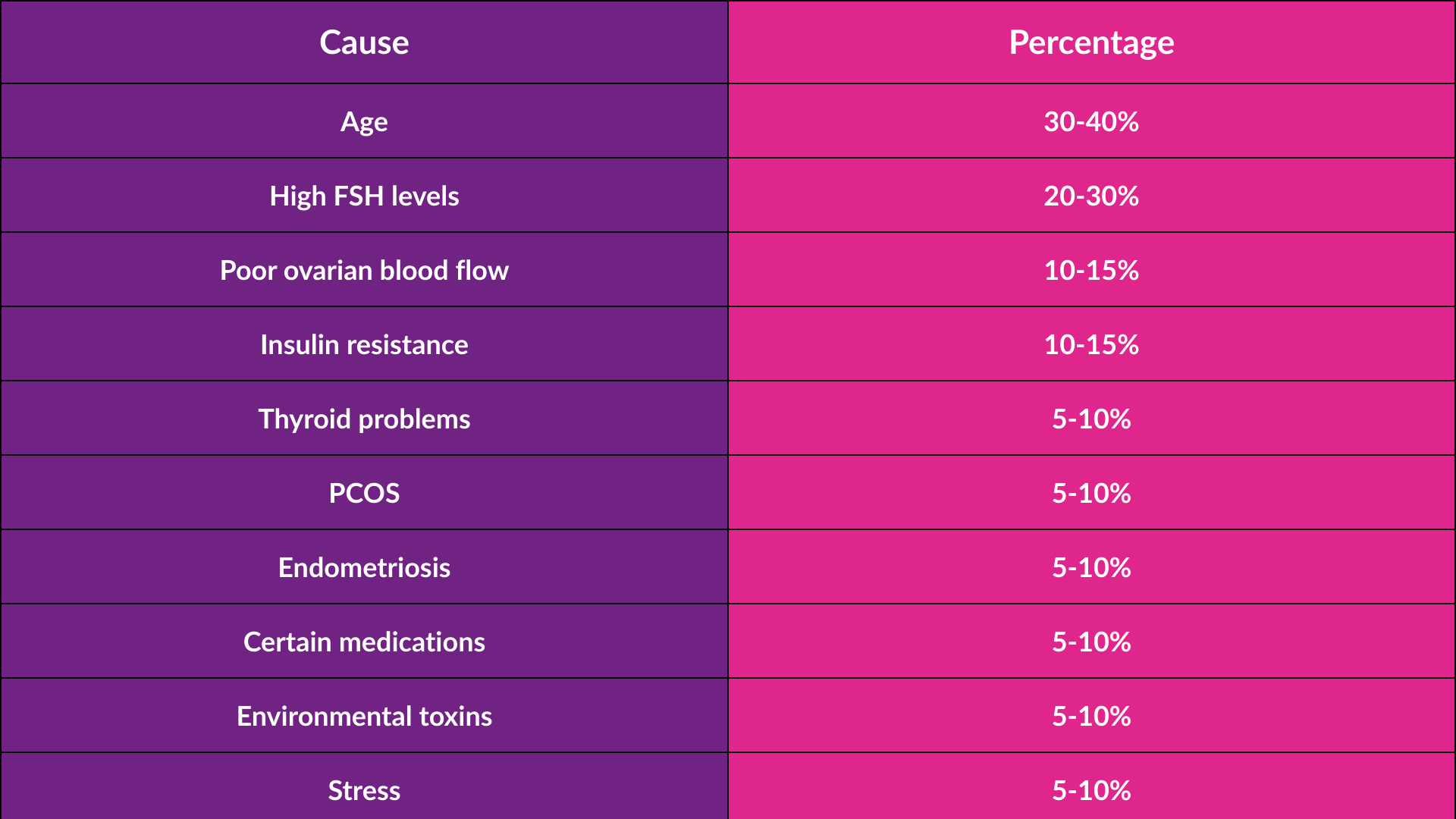

1. Poor Ovarian Reserve
Women with low ovarian reserve (fewer eggs remaining in the ovaries) may experience slow follicular growth due to reduced responsiveness to stimulation medications. This is more common in women over 35 or those with diminished ovarian reserve (DOR).
2. Low Levels of Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
FSH is essential for follicle development. If levels are too low, follicles may not receive enough stimulation to grow at the expected rate. This can be caused by hormonal imbalances or pituitary gland dysfunction.
3. Poor Blood Circulation to the Ovaries
Adequate blood flow to the ovaries ensures that follicles receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen. Conditions like poor circulation, stress, or underlying health issues can lead to sluggish follicle development.
4. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)


PCOS is a common condition that affects ovulation and follicle development. Women with PCOS often have many small follicles that struggle to mature properly, leading to irregular growth and poor egg quality.
5. Over-Suppression from Medications
Certain IVF protocols use birth control pills or GnRH agonists to regulate hormones before stimulation. In some cases, this can lead to excessive ovarian suppression, causing slower follicular growth during stimulation.
6. Poor Egg Quality
Egg quality and follicle growth are closely linked. Aging, lifestyle factors, and genetic abnormalities can impact egg quality, leading to delayed maturation and slow follicular growth.
7. Thyroid Dysfunction

Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism and reproductive function. Hypothyroidism (low thyroid function) can disrupt ovarian stimulation, leading to sluggish follicle growth and poor IVF outcomes.
8. High Androgen Levels
Excess androgens (male hormones) can interfere with normal follicular development. This is common in women with PCOS and can lead to follicular arrest, where follicles stop growing before reaching maturity.
9. Insufficient Stimulation Protocol
If the IVF medication dosage is too low or not suited to an individual’s ovarian response, follicle growth may be slower than expected. Personalized medication adjustments are crucial for optimal stimulation.
10. Lifestyle Factors (Diet, Stress, and Smoking)
Unhealthy lifestyle choices can impact follicle growth:
- Poor diet: Deficiencies in essential nutrients like vitamin D, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids can slow down follicular development.
- High stress levels: Stress affects hormone production, potentially leading to sluggish ovarian response.
- Smoking and alcohol use: Toxins from cigarettes and alcohol can impair egg and follicular development, reducing IVF success rates.
How to Improve Follicular Growth in IVF?
To enhance follicular development and increase the chances of a successful IVF cycle, consider these strategies:
✔ Optimize Hormonal Balance: Work with a fertility specialist to adjust medication protocols based on your ovarian response.
✔ Improve Blood Circulation: Engage in light exercises like yoga, acupuncture, or fertility massage to improve ovarian blood flow.
✔ Address Underlying Conditions: Treat thyroid disorders, PCOS, or hormonal imbalances that may affect follicle growth.
✔ Maintain a Healthy Diet: Include fertility-friendly foods like leafy greens, healthy fats, and lean proteins.
✔ Manage Stress Levels: Reduce stress through relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or counseling.
✔ Consider Supplementation: Some fertility supplements, such as CoQ10 and DHEA, may improve follicle development.
Conclusion
Slow-growing follicles in IVF can be caused by various factors, including hormonal imbalances, ovarian reserve issues, lifestyle factors, and medical conditions like PCOS or thyroid dysfunction. Identifying and addressing these issues can help improve follicular response, increase the number of mature eggs, and enhance the chances of a successful pregnancy.
If you’re experiencing slow follicle growth during IVF, consult with a fertility specialist at Eva IVF Chennai to personalize your treatment plan and optimize your chances of success.
FAQ – Top 10 Reasons for Slow Growing Follicles in IVF


1. How to speed up follicle growth in IVF?
Lifestyle improvements, proper medication adjustments, and addressing underlying health conditions can promote faster follicle development.
2. What causes slow embryo growth in IVF?
Slow embryo growth in IVF can result from factors like poor egg or sperm quality, chromosomal abnormalities, or suboptimal lab conditions. Age, lifestyle, and underlying health issues may also play a role.
3. Are slow-growing follicles better?
Slow-growing follicles are not necessarily better, but they may still produce viable eggs. Consistent monitoring by your fertility specialist is key to assessing their potential.
4. What prevents follicles from growing?
Follicle growth can be hindered by hormonal imbalances, stress, poor blood flow, or conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Your doctor may recommend treatments to stimulate growth.
5. Is 7 follicles good for IVF?
Yes, 7 follicles can be a positive outcome for IVF. While more follicles may increase the chances of success, quality is just as important as quantity.




