What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that your body cannot produce so you should include some foods in your daily routine. They play a vital role in cell structure, brain health, eye development, and controlling inflammation. There are three primary types of omega-3s:
- ALA (Alpha-Linolenic Acid) – found in plant oils like flaxseed and chia.
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic Acid) – primarily in fatty fish.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic Acid) – mainly from fish and crucial for brain and eye function.
Why Should You Include Omega-3 in Your Diet?
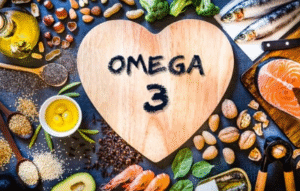
Omega-3s are more than just “healthy fats.” They:
- Support heart health by reducing triglycerides.
- Aid brain function and reduce the risk of cognitive decline.
- Play a role in fetal development, especially DHA during pregnancy.
- Help in managing inflammation, joint pain, and even mood disorders.
Since your body cannot synthesize them, it’s crucial to get them through food or supplements.
Health Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids


Cardiovascular Support
Regular intake reduces bad cholesterol, lowers blood pressure, and supports healthy arteries.
Brain & Cognitive Health
DHA is a major component of the brain and retina which is linked to cognitive decline and poor mental function.
Inflammation Reduction
Omega-3s help counteract chronic inflammation, supporting arthritis and autoimmune conditions.
Prenatal & Infant Development
DHA plays a crucial role in fetal eye and brain development during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Eye Health
Supports visual function and may reduce the risk of macular degeneration and dry eye syndrome.
Top 10 Omega-3 Rich Foods to Add to Your Diet


Here’s a science-backed list with nutrient breakdown and serving suggestions:
| Food | Type of Omega-3 | Content per Serving | Key Nutrients | How Often to Eat |
| 1. Salmon (Wild) | EPA + DHA | ~2,150 mg per 100g | B12, D, Selenium | 2–3 times/week |
| 2. Mackerel | EPA + DHA | ~4,580 mg per 100g | Selenium, B12 | 1–2 times/week |
| 3. Sardines (Canned) | EPA + DHA | ~1,460 mg per 100g | Calcium, B12, D | 1–2 times/week |
| 4. Flaxseeds (Ground) | ALA | ~2,350 mg per tbsp | Fiber, Magnesium | Daily (1 tbsp) |
| 5. Chia Seeds | ALA | ~5,050 mg per 28g | Fiber, Protein | 3–4 times/week |
| 6. Walnuts | ALA | ~2,570 mg per 28g | Vitamin E, Copper | Daily (a handful) |
| 7. Anchovies | EPA + DHA | ~2,000 mg per 100g | Niacin, Selenium | Weekly |
| 8. Cod Liver Oil | EPA + DHA | ~2,400 mg per tbsp | Vitamins A & D | 3–4 times/week (as supplement) |
| 9. Edamame (Soybeans) | ALA | ~670 mg per ½ cup | Folate, Iron | Weekly |
| 10. Algae Oil | EPA + DHA | ~400–500 mg per dose | Plant-based DHA | Daily (for vegans/vegetarians) |
Final Thoughts: Small Changes, Big Impact
Including omega-3 rich foods doesn’t mean a complete diet overhaul. Start small — sprinkle chia on your smoothie, swap your cooking oil with flaxseed oil, or have grilled salmon for dinner once a week.
💡 Whether you’re looking to improve heart health, manage inflammation, or support brain function, omega-3s are non-negotiable. If you’re vegetarian or allergic to fish, plant-based sources and supplements can help you meet your needs.




